Overview of the CSRD
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a European directive that significantly expands sustainability reporting for companies. It replaces the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) and, from 2025, will affect up to 50,000 companies in the EU, including 13,000-15,000 in Germany. The introduction is staggered, beginning with large companies. The CSRD is based on 12 European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and requires a double materiality assessment to ensure comprehensive and transparent reporting on climate, environment, social aspects, and corporate governance.
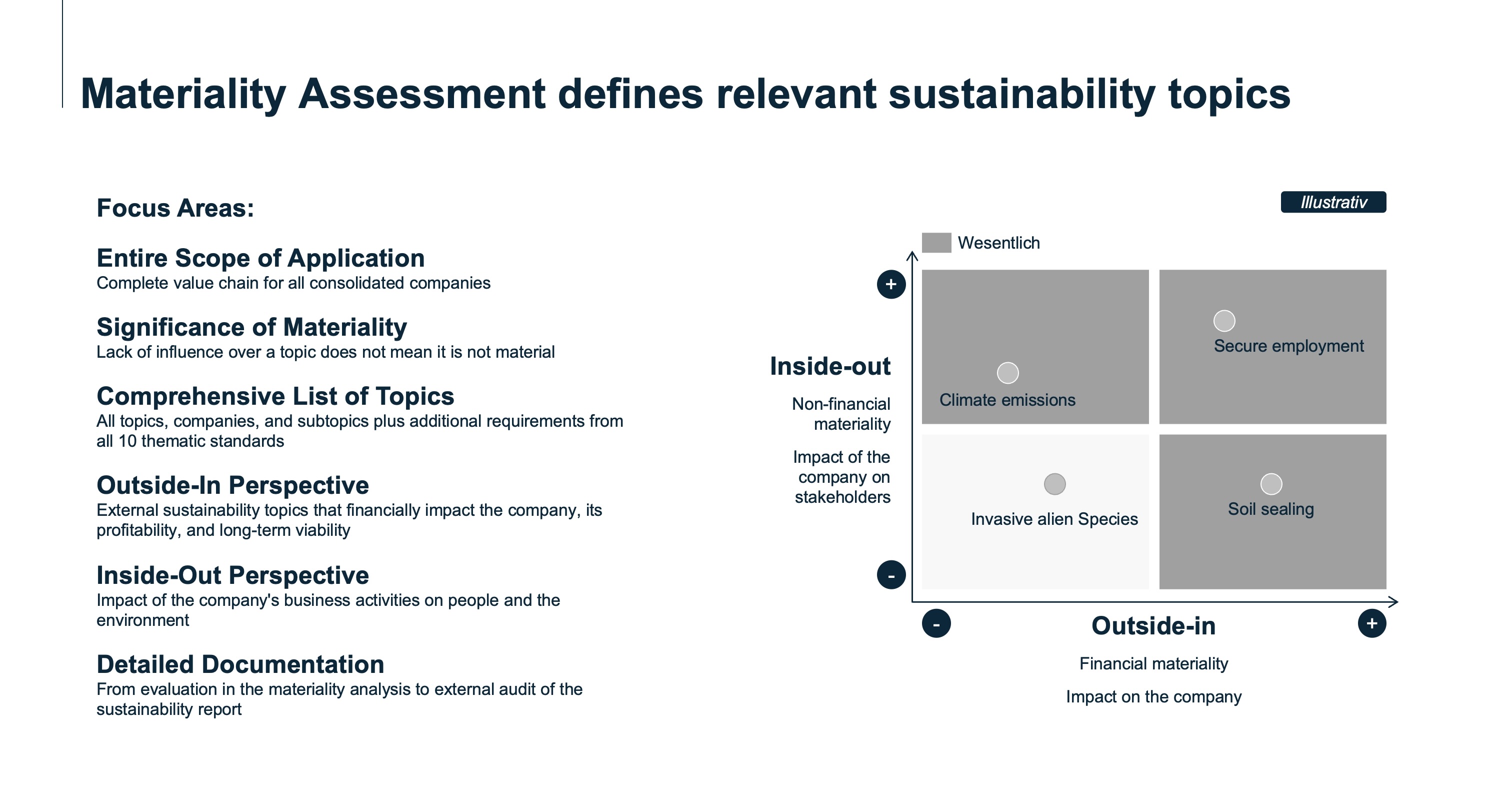
The materiality assessment
The materiality assessment is a central component of sustainability reporting, designed to identify relevant topics that are significant for a company and its stakeholders. This analysis examines which environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects have a material impact on the company and, conversely, what impact the company has on its environment and society.
The concept of double materiality expands this analysis by considering two dimensions: impact materiality and financial materiality. Impact materiality refers to the company’s impact on the environment and society, regardless of whether these impacts have financial consequences. Financial materiality, on the other hand, considers financial risks and opportunities arising from sustainability issues that could affect the company’s financial position.